Strategic outsourcing is the process of engaging the service of a provider to manage essential tasks that would otherwise be managed by in-house personnel. (1) Speaking of this managing tool, people tend to associate it with small companies for small companies usually have limited budget and resources. However, an outsourcing strategy may employed by business and other organizations of any size. Big companies are adapting the tool in their operations too, for arranging the best use of assets to best advantage, and to allow the company to move closer to the achievements of development goals. By outsourcing non-essential parts of work, companies can free valuable resources and focus on their areas of competitive advantage.
After doing some researches, I found many articles are discussing either the functions or the pros and cons about the outsourcing, or examples under the domestic market background. Then I found an article citing in an different perspective that I would like to share with on blog--'Strategic Outsourcing for Sustainable Competitive Advantages: Case Studies of Multi-National Corporations(MNCs) in China'.
http://www.researchgate.net/publication/229051906_Strategic_Outsourcing_for_Sustainable_Competitive_Advantages_Case_studies_of_Multi-National_Corporations_(MNCs)_in_China
It is about the multi-national companies’ outsourcing technology in Chinese business context with the particular focus on strategic outsourcing. For multi-national companies, they usually target at the developing countries as their outsourcing regions, and China is one of the regions. Over the past two decades, China has the significant size of middle and upper class of consumers affording the domestic market, as well as the cost-effective manufacturing opportunities and innovative outsourcing capabilities for multi-national corporations through its vast network of socio-technological resources. According to Chinese Brand Association, the potential size of affluent consumers that purchase high brand product is 160 millions that is about 13% of the total population, reaching 250 million by 2015. (2)
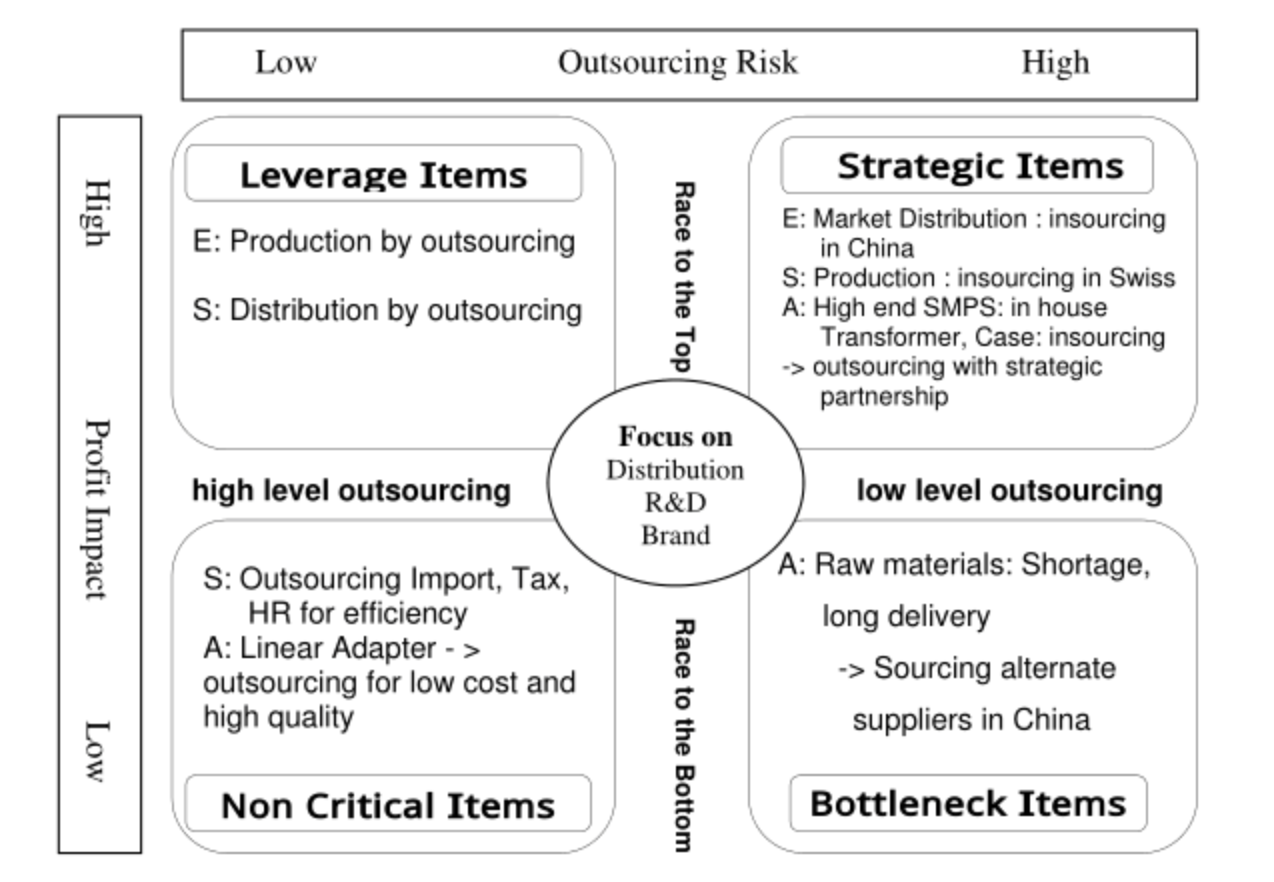
However, except the expanding business opportunities, other potential factors make Chinese market challenging and risky as well. Changes in labor laws, tax regulations and the rise in RMB value affect the multi-national firm’s profit level. Meanwhile, rapidly evolving competitive landscape in China requires new capabilities for global companies. In managing risks and balancing the opportunities, there is a matrix displayed in the article analyzing the patterns of outsourcing in China.
The matrix shows the 4 different patterns—leverage, strategic, non-critical and bottleneck items. The horizontal level is about the degree of outsourcing, and the vertical level is about the strategic direction. Giving out three examples—E-Land, Swatch, Ault, the author match them with each of the categories in the matrix. For the leverage items, E-Land & Swatch outsourced production and distribution functions with high level of outsourcing and they succeed in penetrating Chinese market and exploited the growing buying power. For strategic items, firms controlled the items in house for long term. When strategic items are purchasing items, they made strategic relationship with suppliers. For non-critical items, Swatch outsourced the importing business for efficiency. Ault mainly outsourced low and linear adapters which were marketed mostly in the U.S. and European markets. For bottleneck item, Ault sourced alternate suppliers in China and enhanced cost and delivery competitiveness. Then, the bottleneck items turn to leverage items.
High Level of outsourcing is suitable for leverage and non critical items, and Low level of outsourcing can be applied for strategic and bottleneck items. By doing so, case companies not only reduced the costs, but also enhanced their core business outcomes, being more competitive in the global market.
Here are two questions worth thinking about too:
Q1: What are the impacts of giving up of control of the process of product especially in a foreign country?
Q2: How can we make it not to be too dependent on the outsourcing suppliers?
Reference:
- What is Strategic Outsourcing: http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-strategic-outsourcing.htm
- http://www.researchgate.net/publication/229051906_Strategic_Outsourcing_for_Sustainable_Competitive_Advantages_Case_studies_of_Multi-National_Corporations_(MNCs)_in_China
- http://danielsethics.mgt.unm.edu/pdf/Outsourcing%20DI.pdf
No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.