Lean manufacturing
strategies have been successfully implemented in a wide variety of Industries
other than manufacturing industries.
Amazing examples are from Food chain restaurants such as Subway to
product development in IT Industry.
Lean software overview : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P3A9JPb3KqQ
The
seven principles of lean manufacturing can be applied to optimize the whole IT
value stream. These principles are:
1. Eliminate waste. What’s
a waste? Any activity that does not directly add value to the finished product.
Sources of waste in
software development are the addition of
Unrequired features (
fancy features which is called Gold Plating : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gold_plating_(software_engineering)
Project churn and
Crossing
organizational boundaries (different teams)
Development teams should
be able to self-organize, change plans, quit working for a feature which is
identified as not required.
Reduction of scrap and
rework late in the lifecycle is also required to reduce Project churn.
2. Build in total quality: To build quality software the testing has to
be done for every features and module based. Testing along with development is
the best option if we do not want to see huge number of defects during the
first release. A testing team, aligned with development team can do the job in
a better way. The policy is to build a feature, test it, fix any issues with it
and iterate this for every feature. It is also
called test driven development.
3. Create knowledge. Knowledge management
is critical for a products success. This can be referred to the cross-functional
knowledge between teams and knowledge about what customer or stakeholders want
or what kind of problems we are going to solve. This knowledge gives deeper
visualization and helps to build revolutionary products.
4. Deferring
commitment: It’s probably better to start
development without a complete specification on features and time because we
know scope creep happens. The teams, architecture should be fliexible enough to
adopt any changes.
5. Deliver quickly. Work load
for teams should be limited based on team’s capacity. In Agile based
development the team chooses which functionality to build. Here the time is
fixed. In agile method teams don’t try to do more than they are capable of, but
instead they self-organize and determine what they can build. This way the
teams can actually show valuable deliverables and in less time shippable
product can be made.
6. Engaged people: More productivity
with a higher quality can be achieved only by an engaged work force who think
critically. Higher motivation, less
control over the team can create an engaged work force which is again an idea
comes from agile.
7. Total Optimization: Scrum master or product manager should be
able to view the whole picture supporting the vision. A highly sustainable and high
quality product can be made by managing programs, team, multiple
projects, business processes and interrelated systems, and this way the IT
value stream can be improved.
Here is a video how Toyota Lean strategies are incorporated in Lean software development
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I5gN66KFtaI
Lean process goes well
with agile development though there are multiple similarities and dissimilarities:
The differences are
very technical. Therefore I am proving a link for the people who want to know
the technical differences between agile and lean-
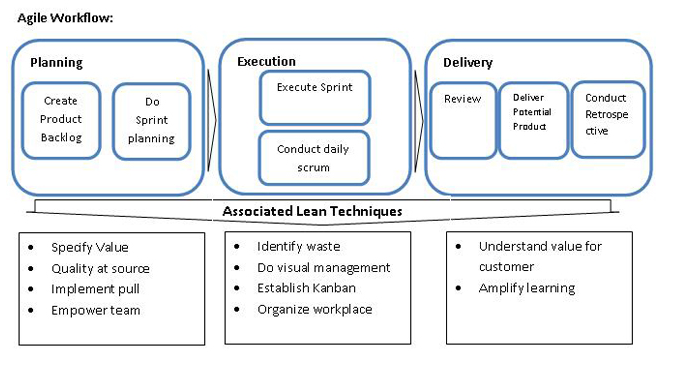
Lean is important for scaling agile in several ways:
1. Lean is probably an
explanation why agile works
2. It provides
techniques for identifying waste
which makes agile more flexible and effective
3. Lean offers insight
into strategies for improving the software process
- Value stream mapping ( Find more http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HKxL_S47yJg)
Can you think of specific types of software products where only Agile or only Lean have more chances of success?
Sources:
Great presentation this very necessary for us to be have the knowledge all about this, really appreciable blog!
ReplyDeleteKaizen Training